Obesity in the USA: A Weighty Concern

1. The Prevalence of Obesity
Obesity is a serious, common, and costly chronic disease in the U.S. More than 2 in 5 American adults grapple with obesity1. Between 2017 and March 2020, the prevalence of obesity among U.S. adults was 41.9%, with severe obesity affecting9.2% of the population1. These numbers have been steadily rising over the years, highlighting the urgency of addressing this health crisis.
2. Lifestyle and Eating Habits
a. Sedentary Lifestyle
- Modern life often involves prolonged sitting—whether at desks, in cars, or on couches. Our bodies were designed for movement, but sedentary habits prevail.
- Lack of physical activity contributes significantly to weight gain and obesity.
b. Fast Food Culture
- The convenience of fast food and processed meals has become a staple in American diets.
- High-calorie, low-nutrient foods are readily available, leading to overconsumption.
c. Portion Sizes
- Supersized portions have become the norm. Restaurants, cafeterias, and even home-cooked meals often exceed recommended serving sizes.
- Portion distortion contributes to excessive calorie intake.
d. Stress and Emotional Eating
- Stress, anxiety, and emotional triggers drive people to seek comfort in food.
- Emotional eating can lead to overeating and weight gain.
3. Health Dangers
Obesity isn’t just about aesthetics; it poses serious health risks:
- Heart Disease: Obesity increases the risk of heart attacks, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular issues.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess weight affects insulin sensitivity, leading to diabetes.
- Joint Problems: Carrying extra weight strains joints, causing pain and limiting mobility.
- Certain Cancers: Obesity is linked to cancers such as breast, colon, and kidney cancer.
- Sleep Apnea: Excess fat can obstruct airways during sleep, leading to sleep apnea.
4. Turning the Tide: Small Efforts, Big Impact
* Balanced Diet
- Prioritize whole foods: fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Control portion sizes and limit processed foods.
* Regular Exercise
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Find activities you enjoy—walking, dancing, swimming, or yoga.
* Mindful Eating
- Pay attention to hunger cues and emotional triggers.
- Avoid mindless snacking.
* Sleep Well
- Lack of sleep disrupts hormones related to hunger and satiety.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
5. Real Data and Analytics
- Annual medical costs for adults with obesity are $1,861 higher per person than those with healthy weight. For severe obesity, the excess costs soar to $3,097 per person1.
- Obesity has more negative health consequences than smoking, drinking, or poverty. Approximately 23% of Americans are obese, and an additional 36% are overweight2.
A CHOICES study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, predicts that by 2030:
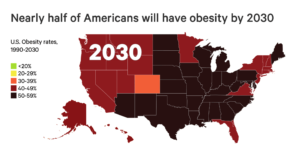
- About half of the adult U.S. population will have obesity.
- Approximately a quarter will have severe obesity.
- Severe obesity is projected to be the most common BMI category in 10 states and certain demographic subgroups12.
The study highlights the health and economic implications of obesity and severe obesity, emphasizing their impact on chronic diseases, medical spending, and life expectancy. Notably, low-income adults are particularly affected, with substantial implications for future Medicaid costs







